Java Access Modifiers
Java Access Modifiers
What are Access Modifiers?
- In Java, access modifiers are used to set the accessibility (visibility) of classes, interfaces, variables, methods, constructors, data members, and the setter methods.
Types of Access Modifier
Before you learn about types of access modifiers, make sure you know about Java Packages.
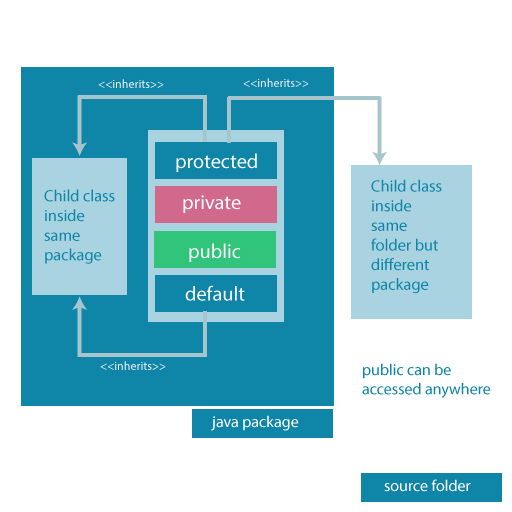
There are four access modifiers keywords in Java and they are:
Modifier Description
Default --> declarations are visible only within the package (package private)
Private --> declarations are visible within the class only
Protected --> declarations are visible within the package or all subclasses
Public --> declarations are visible everywhere
Access Modifier Within class Within package Outside package by subclass only Outside package
Private Y N N N
Default Y Y N N
Protected Y Y Y N
Public Y Y Y Y
Default Access Modifier:
If we do not explicitly specify any access modifier for classes, methods, variables, etc, then by default the default access modifier is considered.
For example:
package defaultPackage;
class Logger {
void message(){
System.out.println("This is a message");
}
}
Private Access Modifier:
When variables and methods are declared private, they cannot be accessed outside of the class.
For example:
class Data {
// private variable
private String name;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] main){
// create an object of Data
Data d = new Data();
// access private variable and field from another class
d.name = "VDS";
}
}
When we run the program, we will get the following error:
Main.java:18: error: name has private access in Data
d.name = "VDS";
Protected Access Modifier:
When methods and data members are declared protected, we can access them within the same package as well as from subclasses.
For example:
class Animal {
// protected method
protected void display() {
System.out.println("I am an animal");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of Dog class
Dog dog = new Dog();
// access protected method
dog.display();
}
}
Public Access Modifier
When methods, variables, classes, and so on are declared public, then we can access them from anywhere. The public access modifier has no scope restriction.
For example:
// Animal.java file
// public class
public class Animal {
// public variable
public int legCount;
// public method
public void display() {
System.out.println("I am an animal.");
System.out.println("I have " + legCount + " legs.");
}
}
// Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
// accessing the public class
Animal animal = new Animal();
// accessing the public variable
animal.legCount = 4;
// accessing the public method
animal.display();
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment